SpringBoot框架
SpringBoot 入门
简介
Spring简化Spring应用开发,约定大约配置,去繁从简整个
Spring技术栈的一个大集合
J2EE开发的一站式解决方案
背景
J2EE笨重的开发、繁多的配置、低下的开发效率,复杂的部署流程、第三方技术集成难度大
解决了什么
Spring全家桶时代Sping Boot=>J2EE一站式解决方案Spring Cloud=> 分布式整体解决方案
优点
- 快速创建独立运行的
Spring项目以及与主流框架集成- 使用嵌入式的
Servlet容器,应用无需达成War包starters自动依赖与版本控制- 大量的自动配置,简化开发,也可修改默认值
- 无需配置
xml,无代码生成- 准生产环境的运行时应用监控
- 与云计算的天然集成
微服务
- 是一种架构风格
- 是一组小型服务,可以通过
HTTP的方式进行沟通
pom.xml 配置
依赖
<parent>
1 | # 导入 parent 依赖 |
<build>
1 | # 导入 Maven 插件 |
<dependencies>
1 | # web 依赖 |
1 | # jdbc 数据库连接依赖 |
1 | # test 单元测试依赖 |
1 | # @ConfigurationProperties 注解依赖 |
依赖分析
1 | <parent> |
而 spring-boot-starter-parent 的父项目是 spring-boot-dependencies
1 | <parent> |
在 spring-boot-dependencies 里有 properties 用来定义每一个依赖的版本
1 | <properties> |
注解
@SpringBootApplication
来表示一个主程序类,说明这是一个 SpringBoot 应用
其内部还有更多注解
@SpringBootConfiguration:表示这是一个配置类
@Configuration配置类类似于配置文件,也是容器中的一个组件@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包,将主配置类所在的包,及其下所有子包的所有组件都扫描进去
@Import({Registrar.class}):底层注解,导入对应组件@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}):给容器中导入组件
@Controller
标在类上,用于表示一个组件
@RequestMapping(“url”)
用来接收 URL 请求
@ResponseBody
用来向客户端返回信息
@RestController
集合了
@ResponseBody和Controller
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “对象”)
标在类上,将从配置文件中获取对象的值,并赋值给该类中的属性
@Value(“${?}”)
标在属性上,直接从配置文件找到对应的配置,将值赋给该属性,取配置的时候不支持松散绑定,并且不支持复杂类型的获取
@PropertySource(“classpath:?”)
标在类上面用于加载指定的配置文件
@ImportResource(locations = {“classpath:?.xml”})
标在主配置类上,用于导入自定义的
Spring配置文件
@Configuration
标在类上,用于表示这是一个配置类
@Bean
标在方法上,表示这是一个
Bean,SpringBoot会将这个Bean加到配置里,Bean的名字就是这个方法名
SpringBoot 配置
YAML
A Markup Language- 是一个标记语言Isn't Markup Language- 不是一个标记语言
语法
1 | key: value # ':' 后面必须有一个空格 |
字面量的表示
1 | # 直接写 |
对象的表示
1 | 对象名: |
数组的表示
1 | 数组名: |
Properties
1 | =值1 |
Profile
在开发中,对于不同的开发环境,总会有不同的配置,我们可以对不同环境进行配置
Properties 配置方式
将三个环境分别写在不同的三个配置文件中
application.properties
application-dev.properties
application-prod.properties其中以
application.properties为默认,如果要更改环境,也要在application.properties里面配置spring.profiles.active='?'来激活,其中,?代表dev或者prod
Yaml 配置方式
在
.yml文件中,通常以 ‘—‘ 为分界线,将上下分为两个不同的文档块,我们可以利用这个来将不同环境的配置写在同一文件下的不同文档块,默认使用没有配置spring: profiles: ?的文档块
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
profiles:
active: ?
spring:
profiles: dev
spring:
profiles: prod其中,
?代表dev或者prod
其他方式
首先,配置文件还是要写好,至于是用
properties方式还是yaml方式写,取决于个人爱好。在其他地方只需要去通过某种方法来启动相应环境即可
命令行方式
当项目打包之后,在命令行运行该
jar包时使用
java -jar ?.jar --spring.profiles.active=?
虚拟机方式
当项目需要在虚拟机中运行时
-Dspring.properties.active=?
配置文件的加载
SpringBoot 指定的位置
- 根目录/config/?
- 根目录/?
- resource/config/?
- resource/?
- 加载顺序,优先级均从上到下并形成互补配置
自定义的位置
这个需要打
jar包后在命令行运行
--spring.config.location=yourpath
其他外部配置位置
优先级从高到低,高的覆盖低的,并形成互补配置
- 命令行参数
- 来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
- Java系统属性( System.getProperties() )
- 操作系统环境变量
- RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
- jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.ym(带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
- jar包内部的application.properties或application.ym(不带spring.profile)配置文件
- @Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
- 通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
自动配置原理
启动
SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类。在@SpringBootApplication开启了自动配置功能@EnableAutoConfiguration
2
3
4
5
6
public class SpringbootStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootStudyApplication.class, args);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// 这里
public SpringBootApplication {
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration
- 而在
@EnableAutoConfiguration中又通过@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})自动导入了组件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 这里
public EnableAutoConfiguration {
}
selectImports()
- 在
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class中,有一个selectImports()的方法,这个方法调用该类下面的getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
DeferredImportSelector,
BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
EnvironmentAware,
Ordered {
// selectImports
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); // 这里
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
}
getAutoConfigurationEntry()
- 在
getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法中又调用该类中的getCandidateConfigurations()方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
DeferredImportSelector,
BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
EnvironmentAware,
Ordered {
// getAutoConfigurationEntry
protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
} else {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); // 这里
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
}
loadFactoryNames()
- 在
getCandidateConfigurations()中调用SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
DeferredImportSelector,
BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
EnvironmentAware,
Ordered {
// getCandidateConfigurations
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); // 这里
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
}
loadFactoryNames()
- 在
SpringFactoriesLoader.class的loadFactoryNames()中调用该类下面的loadSpringFactories()方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// loadFactoryNames
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); // 这里
}
}
loadSpringFactories
- 在
loadSpringFactories()方法里,通过扫描所有jar包下面的META-INF/spring.factories文件。在得到这个文件的url之后,对这个文件进行遍历,获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class的值,并整合成一个properties文件。将结果放在LinkedMultiValueMap result里面进行返回
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// loadSpringFactories
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories( ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
// 结果集
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
// url
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 封装成 properties
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories
- 我们会在
磁盘:\Maven 仓库路径\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-autoconfigure\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\spring.factories中找到它遍历的内容,这就是自动配置之源
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudServiceConnectorsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.rest.RestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
加载组件
以
HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration为例,在这个类上有 5 个注解这个自动配置类意思就是根据当前不同条件判断,决定这个判断是否生效
其中有一些属性需要从配置文件中获取值,而配置文件已经通过某个属性,形成了对应关系。比如这个
HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration里面有一个properties,这个属性是通过有参属性拿到的,而参数则是从@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})注解中拿到
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
private final Encoding properties;
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
}
- @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
- 用于表示这是一个配置类
- @EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class})
- 启用
ConfigurationProperties功能,打开HttpProperties.class会发现这个类标注了@ConfigurationProperties注解,这个注解就是从配置文件获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定,并把HttpProperties加入到容器中
2
3
public class HttpProperties {
}
- 到此,我们就可以参考该类里面的属性,对配置做出精确修改,比如在这个类中有
Encoding这个内部类,就可以通过spring.http.encoding.charset来配置字符编码,前面的spring.http来自于注解上的前缀prefix = "spring.http"
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class HttpProperties {
public static class Encoding {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET;
private Charset charset;
private Boolean force;
private Boolean forceRequest;
private Boolean forceResponse;
private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping;
}
}
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
- 根据条件不同,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效
- @ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class})
- 判断当前项目有没有这个类
- @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = “spring.http.encoding”, value = {“enabled”}, matchIfMissing = true)
- 判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置,这里判断的是
spring.http.encoding.enable,而matchIfMissing = true意思就是说,如果没有则默认生效
Conditional
| 注解 | 作用 |
|---|---|
@ConditionalOnJava |
系统的 Java 是否符合要求 |
@ConditionalOnBean |
容器中存在指定的 Bean |
@ConditionalOnMissingBean |
容器中没有指定的 Bean |
@ConditionalOnExpression |
满足 SpEL 表达式 |
@ConditionalOnClass |
系统中有指定的类 |
@ConditionalOnMissingClass |
系统中没有指定的类 |
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate |
容器中只有一个指定的 Bean,或者这个是首选 Bean |
@ConditionalOnProperty |
系统中的属性是否有指定的值 |
@ConditionalOnResource |
类路径下是否存在指定的资源文件 |
@ConditionalOnWebApplication |
当前是 web 环境 |
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication |
当前不是 web 环境 |
@ConditionalOnJndi |
JNDI 存在指定项 |
自动配置报告
因为自动配置类都是需要满足一定条件才能生效,所以一开始并不会加载所有自动配置类。我们需要知道哪些自动配置类起作用,才能精确做出相应配置
我们可以在核心配置文件中进行配置:
debug = true,当项目启动时,在控制台就会有自动配置报告,显示出哪些自动配置类启用了,哪些自动配置没启动
日志
SLF4j的使用原理
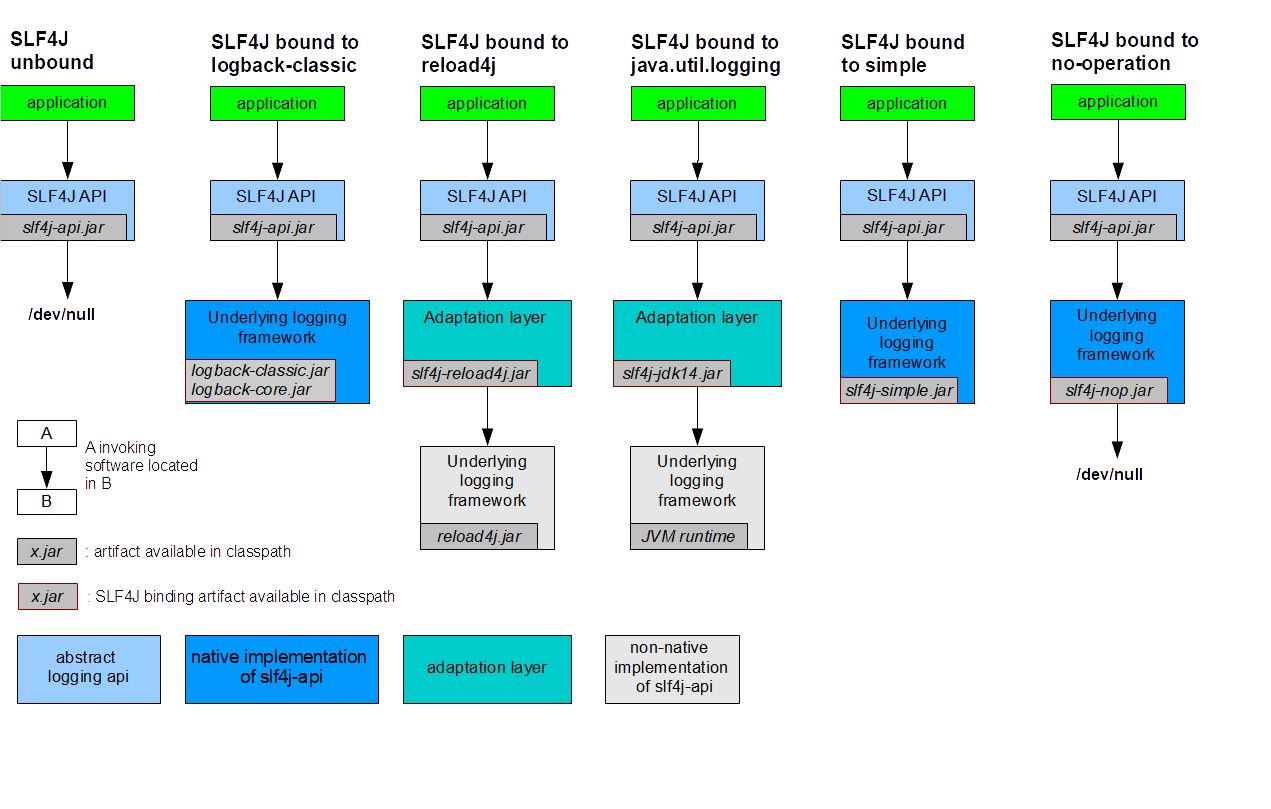
统一日志框架
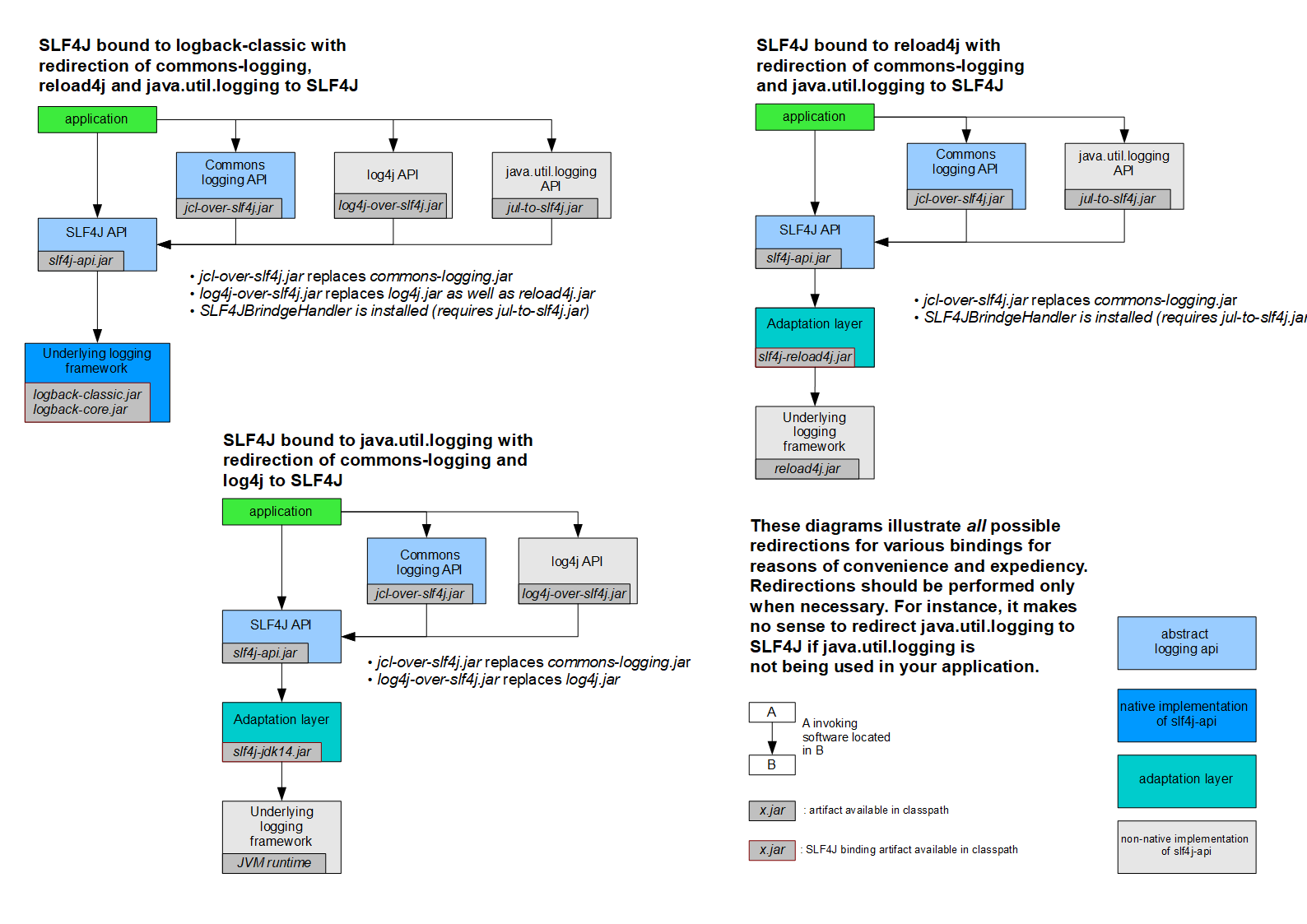
- 将系统中的其他日志框架排除
- 用中间包来替换原有的日志框架
- 导入
slf4j的其他实现
SpringBoot 日志关系

使用日志
1 | Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); |
logging.level.包路径 = 级别
调整日志的级别
logging.file=磁盘:/路径/?.log
在指定位置生成日志文件
logging.path=路径
在当前磁盘的根目录,根据指定路径创建名为
spring.log的日志文件
logging.parttern.console=?
设置在控制台的打印信息
日志输出格式
- %d 日期
- %thread 线程名
- %-5level 左对齐
- %logger{50} logger 名最长 50 个字符否则按照句点分割
- %msg 日志消息
- %n 换行符
logging.parttern.file=?
设置在文件中的打印信息
高级特性
如需自己去配置日志文件,可参照下表,在
classpath中建立相应文件进行配置
| 日志系统 | 自定义配置文件 |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml or logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
SpringBoot官方建议当我们使用logback日志系统时在配置文件名后面加一个-spring的后缀,因为在加载的过程中,日志系统能直接识别logback.xml,这样虽然没问题,但是直接绕过了SpringBoot,当我们加上-spring后缀之后,日志系统就不能直接识别这个配置文件,该文件就会由SpringBoot进行处理,在这种情况下,我们就能使用SpringBoot日志系统的一个高级特性 —— 在不同的profile环境设置不同的输出配置
2
3
4
5
</springProfile>
// ?: dev/prod/root
Web 开发
静态资源映射规则
静态资源
有关
Web开发的相关配置都在WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class中,其中的addResourceHandlers()方法指定了访问的路径
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disable d");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}
- 该方法限定了所有
/webjars/**的访问,都去/META-INF/resources/webjars/里面找webjars以jar包的形式导入静态资源- 该方法还限定了自己的静态资源在哪里找,
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()通过这个方法获取到/**即:不是/webjars/**时的处理方法,又通过this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()获取到了这个访问方法的访问路径、
2
3
4
"classpath:/resources/"
"classpath:/static/"
"classpath:/public/"欢迎页
在
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class中有WelcomePageHandlerMapping()方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService,
ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}在这个方法里又调用
getWelcomePage()方法和getStaticPathPattern()方法,分别获取欢迎页和它的映射路径
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
String[] locations = WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
return Arrays.stream(locations).map(this::getIndexHtml).filter(this::isReadable).findFirst();
}
private Resource getIndexHtml(String location) {
return this.resourceLoader.getResource(location + "index.html");
}
2
3
return this.staticPathPattern;
}我们可以发现,欢迎页就是
staticPathPattern下的***.index文件





